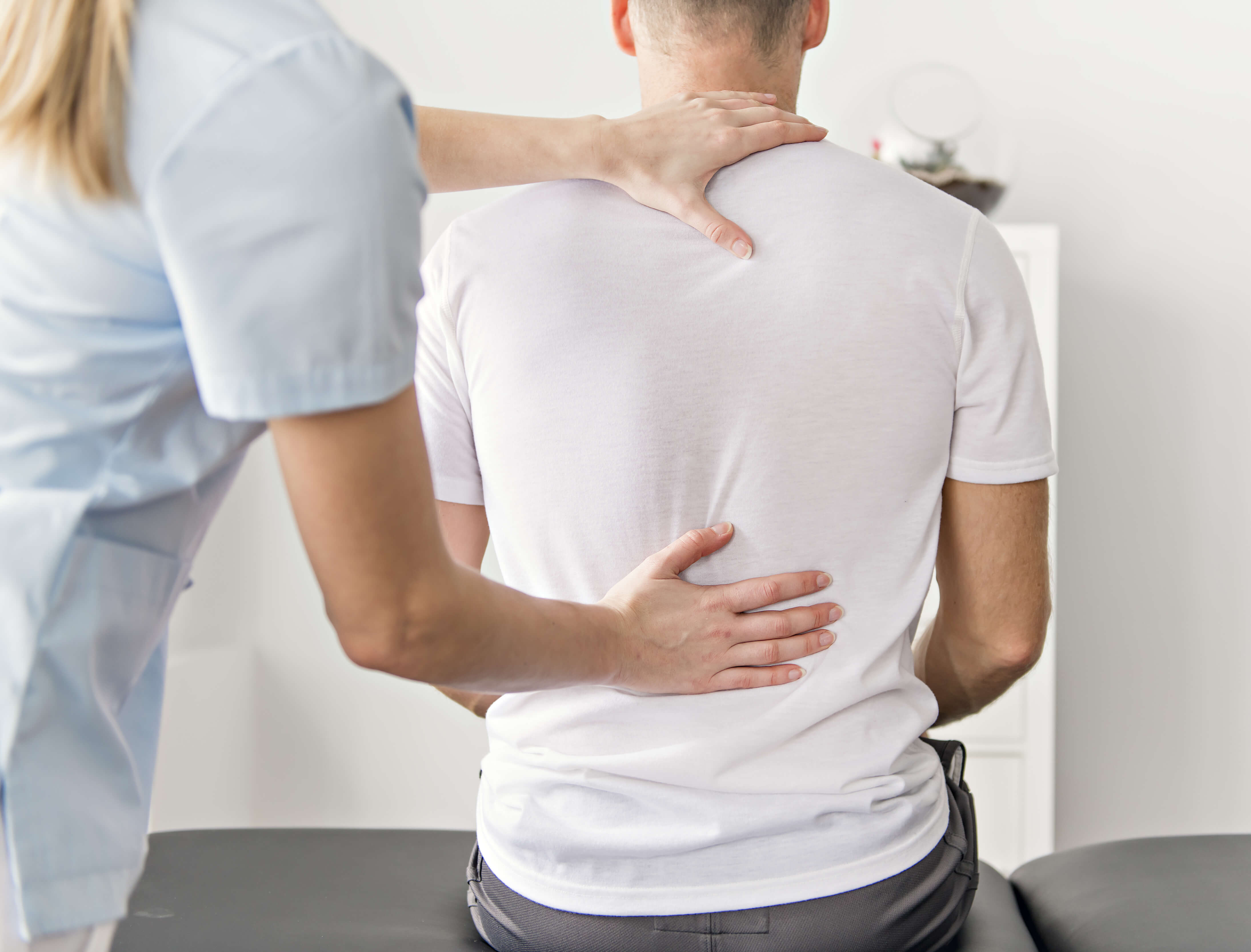
Back pain is a common problem among the United States population as it affects approximately 16 million adults. While older people are more susceptible to back pain, it can also strike at a younger age. People describe the pain differently – some reporting it as a muscle ache, a stabbing, burning, or shooting sensation. Most of the time, lower back pain improves with self-care measures such as gentle exercises and heart compressions. However, sometimes, the pain can be debilitating, making it necessary for you to visit Dr. Adam Camp for advanced treatment.
What causes back pain?
- Muscle strains and sprains. These are common injuries that usually result from heavy lifting or sudden, awkward movements. Strains can affect the ligaments, tendons, and muscles in your lower back resulting in pain.
- Fractures. The bones in your lower back may break due to a car crash or a fall from a high place. Older adults are more susceptible to fractures since their bones are usually weak and brittle. Medical conditions such as osteoarthritis also increase one’s risk of fractures.
- Spinal stenosis. It is a structural problem of the spine that develops due to a narrowing of the spinal space. A narrow spinal column may cause nerve compression resulting in symptoms such as pain, muscle weakness, tingling, and loss of sensation in the legs.
- Herniated discs. The bones that make up the spinal cord comprise discs that hold the spine in place and act as a shock absorber. These discs have a tough outer covering which can develop a weak spot as you grow older or due to wear and tear. When this happens, the inner contents of the disc can bulge into the spinal space and press on nerves. The result can be painful, but some have herniated discs with no lower back pain.
Risk factors for back pain
Although anyone, including children, can develop back pain, the following factors increase your problem chances.
- Obesity. When you weigh more than you should, your body puts extra stress on your back, which can cause back pain.
- Physical inactivity. Exercise helps in strengthening your muscles and improving flexibility. Lack of exercise makes your muscles weak and more susceptible to strains.
- Medical conditions. Diseases such as osteoarthritis and bone cancer are associated with lower back pain.
- Smoking. Smoking limits blood flow in the bones in your body, including those of the spine. Limited blood supply translates to inadequate oxygen, which makes the bones brittle. Individuals who smoke are at risk of osteoporosis and other health problems, including lung cancer.
- Mental disorders. Patients with psychological conditions like depression and anxiety are more likely to develop back pain than other populations.
Treatment for back pain
Most back pain gets better with simple remedies such as over-the-counter pain relievers, cold and hot compresses, and rest. However, specialists do not recommend total bed rest since it can worsen the problem. Your doctor may also use other medications such as muscle relaxants, opioids, antidepressants, and topical pain relievers. Physical therapy, steroid injections, and radiofrequency neurotomy also treat back pain. Patients with unrelenting pain due to structural problems may require surgery.
If you have further questions about lower back pain, consult your doctor today at Advanced Pain Solutions.