One of the ways doctors deal with irregular heart rhythm is by inserting a pacemaker into a patient’s chest to help regulate electrical activity in the heart. In many cases, an irregular heartbeat, especially one that causes the heart to beat slowly, can cause cardiac complications, which can be life-threatening. The right location for doctors to place a pacemaker in Houston to restore functionality in the heart is just below the collarbone.
What is the heart’s electrical system?
The heart is a muscle whose function depends on electrical current stimulation. The electrical current flows through specific circuits that begin at the sinoatrial (SA) node.
The location of the sinus or sinoatrial node is at the right upper chamber (atrium) of the heart. The electrical impulse at the SA node is what stimulates heartbeat to 60-100 times per minute for grown-ups. However, this rate of electrical stimulus happens under normal rest conditions.
Upon leaving the SA node, the electric impulse travels to the bottom of the same chamber (right atrium), a place called the atrioventricular (AV) node. Afterward, the impulse travels through the Bundle of His then the His Purkinje system before moving on to the ventricles.
The electrical impulse stimulates ventricular muscles to contract and pump blood throughout the rest of the body. The electrical stimulation coupled with muscle contraction makes up a heartbeat.
If a patient’s heart has complications in the electrical conduction system, a doctor may recommend a pacemaker to help regulate heartbeat.
What are the parts of a pacemaker?
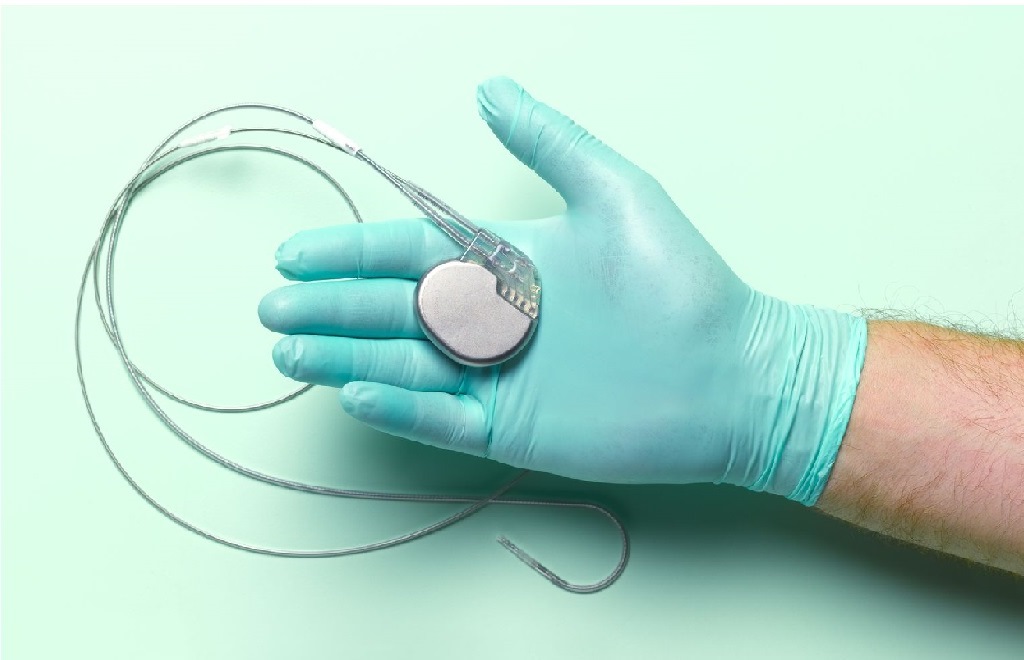
A pacemaker is an electronic device that signals the heart to beat every time a delay or irregularity is in electrical conduction. For a pacemaker to function optimally, three parts contribute towards its structure:
Pulse generator: This small metal case generates the necessary electrical impulse for conduction to occur. Apart from the electrical circuit, there is also a minicomputer and battery that regulate electrical impulses before sending them to the heart.
Lead(s) and electrodes: Your doctor will use this insulated wire with electrodes on the ends to create a connection between the pulse generator and the chambers of the heart. This process will depend on the patient’s medical condition because a doctor may decide to place electrodes on the upper or lower chambers of the heart. Most doctors will run the wire through a large vein that leads to the heart, and place the electrode on the wall of the heart. The lead functions as an electrical impulse delivery system from the pulse generator to the heart. Moreover, the lead acts as a sensor and relays information about the heart’s electrical activity to the pulse generator.
Pacemaker insertion may be what you need to restore heart function. It is important to work with a certified specialist who will correctly place the pacemaker in your chest, and conduct follow-up sessions to monitor your pacemaker’s activity, and adjust the setting when necessary. If you have heart failure, contact Percy F Morales, MD, to determine if pacemaker insertion is a treatment option for you.